

Panchakarma is a Sanskrit word that means"five actions" or "five treatments". This is a process used to clean the body of toxic materials left by disease and poor nutrition. Normally the body has the innate ability to efficiently process and remove these waste materials, including the vitiated doshas. However due to one's repeated dietary indiscretions, poor exercise patterns, lifestyle, and genetic predisposition the digestive enzymes, metabolic co-factors, hormones, and agnis which regulate the body's internal homeostasis become disorganized. This can lead to the accumulation and spread of toxins throughout the physiology resulting in disease. This waste matter is called ama in Ayurveda. Ama is a foul-smelling,sticky, harmful substance that needs to be completely evacuated from the body .
Panchakarma will remove the excess doshas and correct imbalances in them as well as eliminate the harmful ama out of your system through the body's own organs and channels of elimination (colon, sweat glands, lungs, bladder, urinary tract, stomach, intestines,etc). Panchakarma purifies the tissues at a very deep level. It involves daily massages and oil baths and is a very pleasurable experience. Ayurveda recommends Panchakarma as a seasonal treatment for maintaining mental and physical hygiene and balance.
Panchakarma is a five-fold therapy; it is highly individualized based on the needs of the individual depending on the Ayurvedic constitutional type, doshic imbalances, age, digestive strength, immune status, and many other factors. Depending on each individual's needs all or only parts of the five therapies are utilized. These procedures must be administered by specially trained therapists in a definite sequence for a specified period of time. In addition, although Panchakarma is for the most part a delightful and comfortable therapy, there can be periods of discomfort associated with the profound release of toxins which does occur. It is therefore essential that the therapy be supervised by a knowledgeable expert who can recognize the signs of properly and improperly administered Panchakarma. Fortunately these signs were meticulously recorded by the ancient vaidyas.
The purvakarma procedures are often under appreciated in the grand scheme of proper administration of Panchakarma.The general purpose of the Poorvakarma Therapies is to begin to loosen, liquefy, and move the vitiated doshas from their abnormal sites in peripheral tissues to the appropriate central site within the alimentary canal. Oil massage andfomentation are administered on the night before the day of Vamana. Prior to the start of Vamana, the patient is asked to drink a specified quantity of ghee or oil until the stool becomes oily, or nausea occurs. If vamana is planned a Kapagenic diet is given during this time to aggravate Kapha. Either during the same time period or for one week subsequently, oil massages are given..

This treatment is used when there is congestion in thelungs causing repeated attacks of bronchitis, cough, cold or asthma. The objective of thetherapy is to induce vomiting to get rid of the mucus causing excess kapha. On the morning of the vamana., kapha aggravating foods such asbasmati rice and yogurt with salt is given to further aggravate the kapha. The application of theheat to the chest and back will help liquefy kapha. A drink consisting of madanaphalam,licorice and honey, or calamus root tea is given to the patient (other substances used include salt, and cardamom). Vomiting will either occur spontaneously or is induced by rubbing on the tongue.Between 4-8 vomiting evacuations is the target. After vomiting the patient will feel very comfortable; most ofthe congestion, wheezing and breathlessness will disappear along with the clearing of thesinus.
Therapeutic vomiting is used for cough, cold, symptoms ofasthma, fever, nausea, loss of appetite, anemia, poisoning, skin diseases, diabetes,lymphatic obstruction, chronic indigestion, edema (swelling), epilepsy (between attacks),chronic sinus problems and for repeated attacks of tonsillitis.
Virechana is the cleansing of the pitta and the purificationof the blood toxins. Generally, it is administered three days after the Vamana treatment but this may vary. If Vamana therapy is not needed, Virechana can be administered directly after purvakarma. Virechan cleansesthe sweat glands, small intestine, colon, kidneys, stomach, liver and spleen. A number of effective and safe herbs can be used as a laxative. This include senna, prune, bran, flaxseed husk, dandelion root, psyllium seed, cow's milk, salt, castor oil, raisins and mango juice. Whentaking these laxatives, it is important to adhere to restricted diet. Virechana is used fortreatment of skin diseases, chronic fever, piles, abdominal tumors, worms, gout, jaundice,gastrointestinal problems, constipation and irritable bowel syndrome.
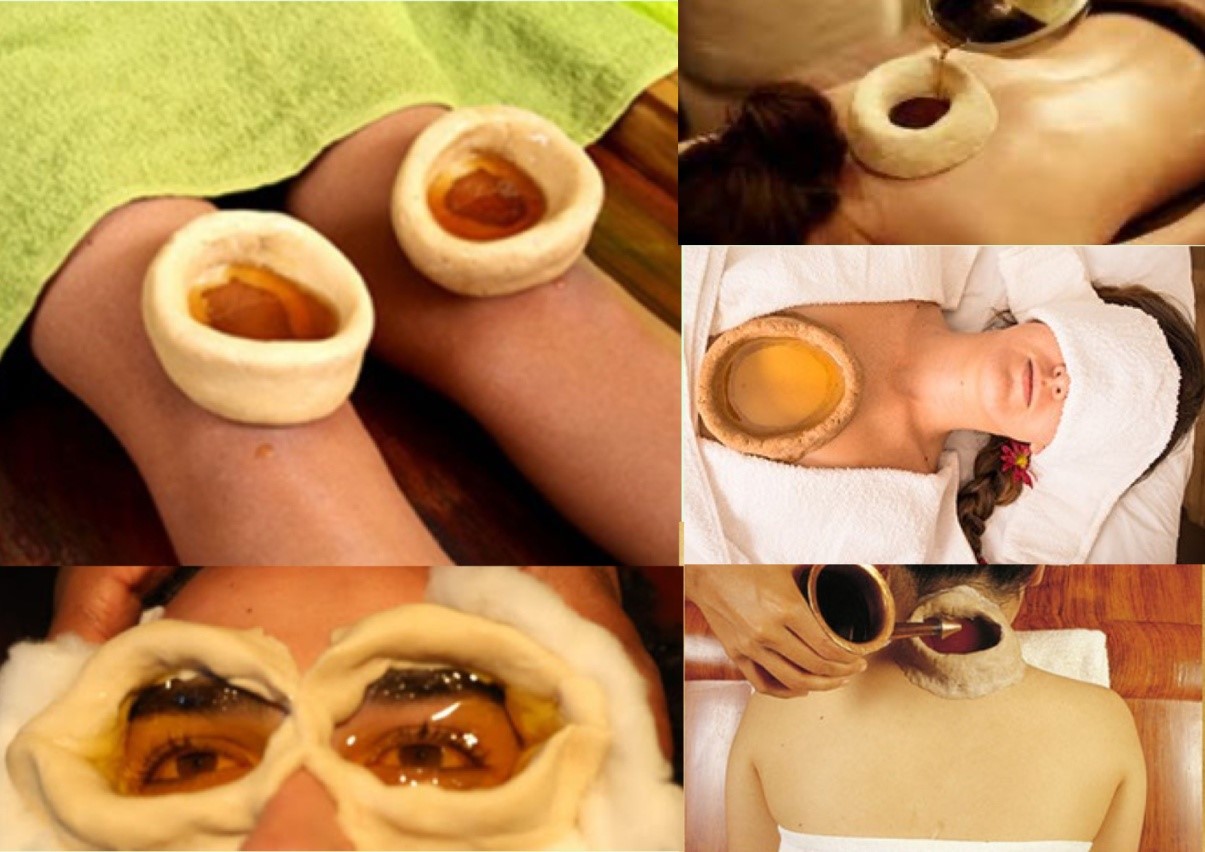


Medicated enemas are used for various specific reasons. In general, this treatment is used topromote elimination of the loosened Vata dosha out through the rectum. There are many specific enemas listed in Ayurveda.
Basti involves introducing medicinal substances such as herbalized oils and other herbal decoctions in a liquid medium into the rectum. Basti is especially good for vata disorders. It alleviates constipation, distention,chronic fever, the common cold, sexual disorders, kidney stones, heart pain, vomiting, backache, neck pain and hyperacidity. Such vata disorders as sciatica, arthritis, rheumatism, neurodegenerative conditions, and gout can also be treated by Basti. There are about 80 vata-related disorders in Ayurveda. About 80 percent of them can be treated with medicated enemas.
Since vata is mainly located in the colon and bones, the medication is administered rectally.
Types of Enemas:
Enemas should not be given to persons suffering from shortness of breath, chronic abdominal pain, bleeding from rectum, cough, diarrhea,severe anemia,the very elderly or to children under 8.
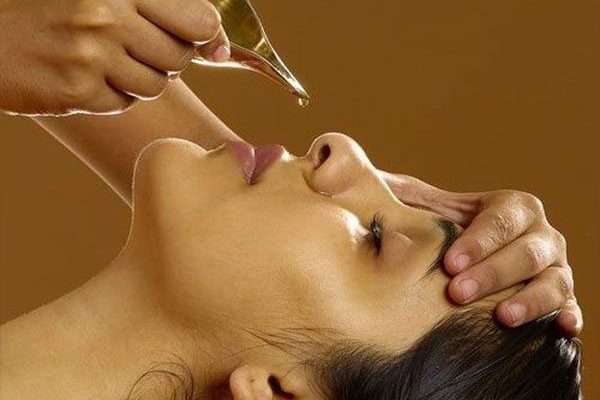
This treatment involves the administation of herbalized oils and liquids into the nostrils. It is useful for treatment of kapha-oriented problems, of ear, eyes, nose and throat disorders such as migraine, sinusitis, catarrh, and bronchitis.
The nose is the gateway to the brain and to consciousness.Prana or vital energy enters the body through breath taken in through the nose. Nasal administration of medication helps to correct the disorders of prana affecting the higher cerebral, sensory and motor functions. Nasya is indicated for dryness of the nose, sinus congestion, hoarseness, migraine headache, neurodegenerative conditions (i.e. multiple sclerosis), convulsions and certain eye and ear problems.
Types of Nasya
Substances such as calamus powder, gotu kola, onion, garlic, black pepper, cayenne, ginger, ghee oil decoctions are used in Nasya. Nasalmedication should not be administered after a bath, food, sex, drinking alcohol, during pregnancy or menstruation.
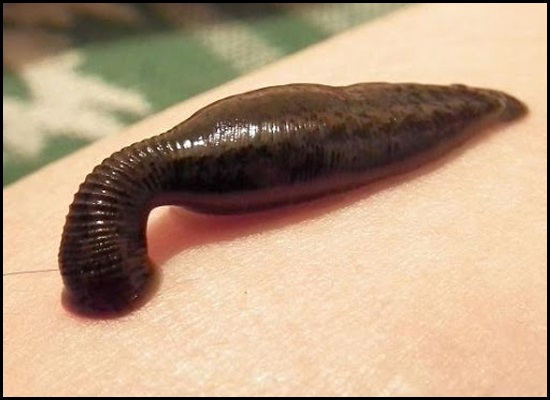


Blood letting is used to eliminate toxins that are absorbedinto the bloodstream through the gastrointestinal tract. This process purifies the blood.It is used for disorders such as repeated attacks of skin disorders such as urticaria, rash, eczema, acne, scabies, leucoderma, chronic itching and hives. It is also often effective for enlarged liver and spleen, hemochromatosis, and for gout.
Blood letting, which should only be administered by aqualified physician, is useful to relieve several pitta disorders such as acne and rash. If administered properly, it stimulates the antitoxic substances in the blood stream, thus developing the immune mechanism in the blood system.
Do not administer blood letting in cases of anemia, edema,weakness or to very old and very young persons.